Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc.
156
Unit 1 Health Informatics Career Pathway
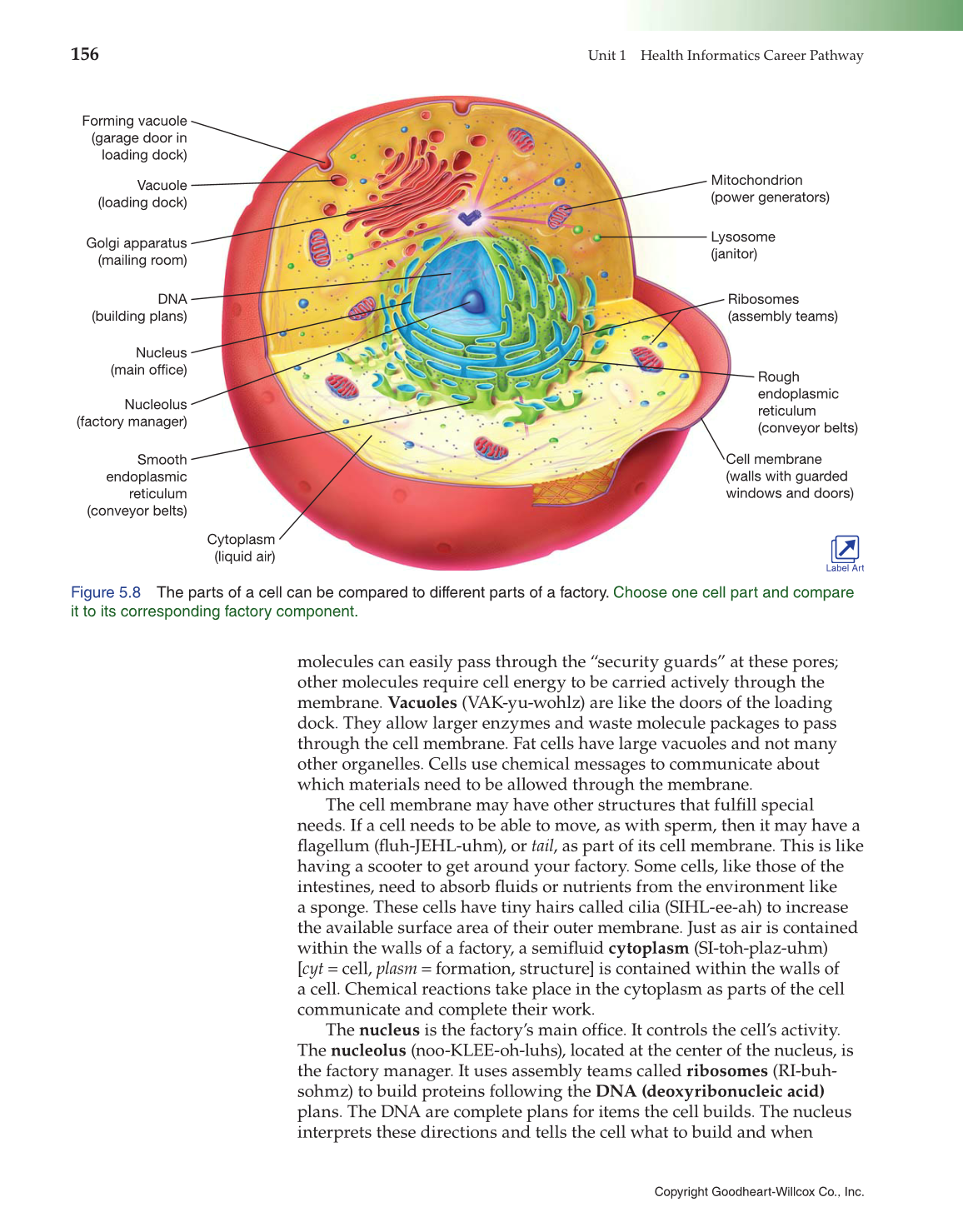
molecules can easily pass through the “security guards” at these pores;
other molecules require cell energy to be carried actively through the
membrane. Vacuoles (VAK-yu-wohlz) are like the doors of the loading
dock. They allow larger enzymes and waste molecule packages to pass
through the cell membrane. Fat cells have large vacuoles and not many
other organelles. Cells use chemical messages to communicate about
which materials need to be allowed through the membrane.
The cell membrane may have other structures that fulfi ll special
needs. If a cell needs to be able to move, as with sperm, then it may have a
fl agellum (fl uh-JEHL-uhm), or tail, as part of its cell membrane. This is like
having a scooter to get around your factory. Some cells, like those of the
intestines, need to absorb fl uids or nutrients from the environment like
a sponge. These cells have tiny hairs called cilia (SIHL-ee-ah) to increase
the available surface area of their outer membrane. Just as air is contained
within the walls of a factory, a semifl uid cytoplasm (SI-toh-plaz-uhm)
[cyt = cell, plasm = formation, structure] is contained within the walls of
a cell. Chemical reactions take place in the cytoplasm as parts of the cell
communicate and complete their work.
The nucleus is the factory’s main offi ce. It controls the cell’s activity.
The nucleolus (noo-KLEE-oh-luhs), located at the center of the nucleus, is
the factory manager. It uses assembly teams called ribosomes (RI-buh-
sohmz) to build proteins following the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
plans. The DNA are complete plans for items the cell builds. The nucleus
interprets these directions and tells the cell what to build and when
Figure 5.8 The parts of a cell can be compared to different parts of a factory. Choose one cell part and compare
it to its corresponding factory component.
Lysosome
(janitor)
Golgi apparatus
(mailing room)
Forming vacuole
(garage door in
loading dock)
Vacuole
(loading dock)
Nucleus
(main office)
Nucleolus
(factory manager)
DNA
(building plans)
Cytoplasm
(liquid air)
Smooth
endoplasmic
reticulum
(conveyor belts)
Rough
endoplasmic
reticulum
(conveyor belts)
Ribosomes
(assembly teams)
Mitochondrion
(power generators)
Cell membrane
(walls with guarded
windows and doors)
Label Art