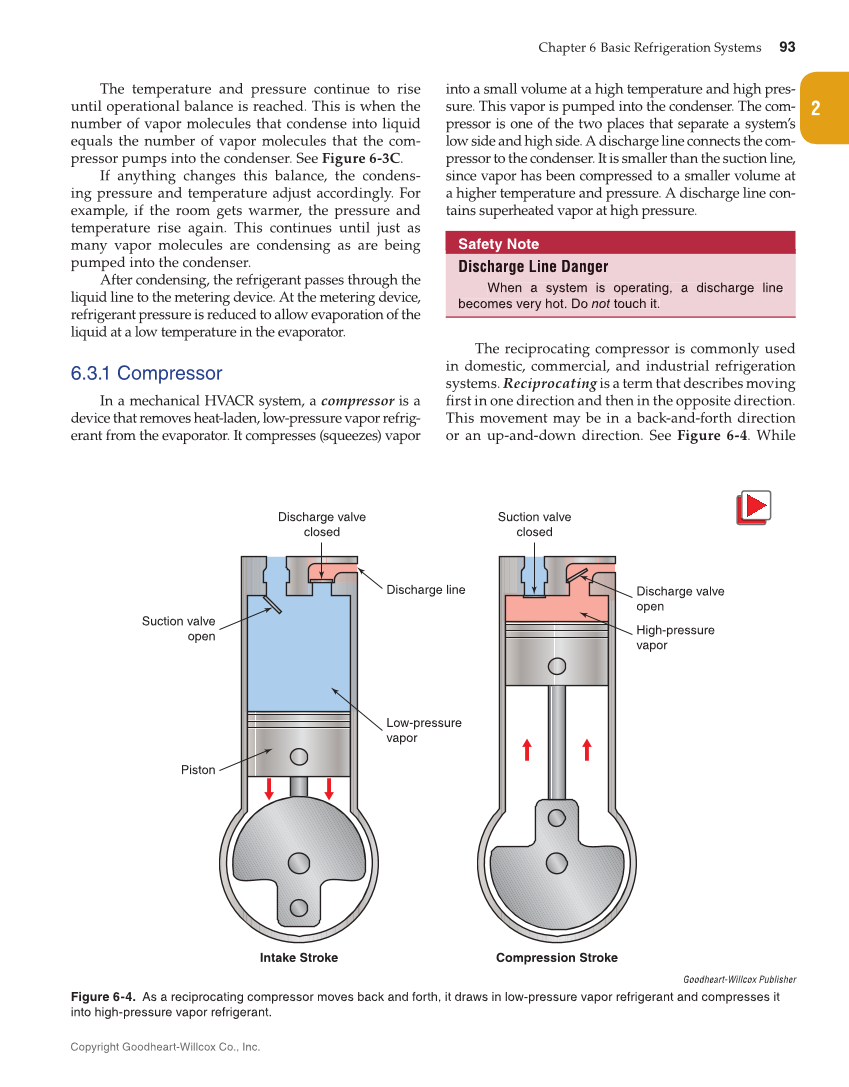
Chapter 6 Basic Refrigeration Systems 93 Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. 2 The temperature and pressure continue to rise until operational balance is reached. This is when the number of vapor molecules that condense into liquid equals the number of vapor molecules that the com- pressor pumps into the condenser. See Figure 6-3C. If anything changes this balance, the condens- ing pressure and temperature adjust accordingly. For example, if the room gets warmer, the pressure and temperature rise again. This continues until just as many vapor molecules are condensing as are being pumped into the condenser. After condensing, the refrigerant passes through the liquid line to the metering device. At the metering device, refrigerant pressure is reduced to allow evaporation of the liquid at a low temperature in the evaporator. 6.3.1 Compressor In a mechanical HVACR system, a compressor is a device that removes heat-laden, low-pressure vapor refrig- erant from the evaporator. It compresses (squeezes) vapor into a small volume at a high temperature and high pres- sure. This vapor is pumped into the condenser. The com- pressor is one of the two places that separate a system’s low side and high side. A discharge line connects the com- pressor to the condenser. It is smaller than the suction line, since vapor has been compressed to a smaller volume at a higher temperature and pressure. A discharge line con- tains superheated vapor at high pressure. Safety Note Discharge Line Dangerr When a system is operating, a discharge line becomes very hot. Do not touch it. The reciprocating compressor is commonly used in domestic, commercial, and industrial refrigeration systems. Reciprocating is a term that describes moving first in one direction and then in the opposite direction. This movement may be in a back-and-forth direction or an up-and-down direction. See Figure 6-4. While Discharge Line Dange When a system is operating, a discharge line becomes very hot. Do not touch it. t Discharge valve closed Suction valve closed Discharge line Discharge valve open High-pressure vapor Low-pressure vapor Suction valve open Piston Intake Stroke Compression Stroke Goodheart-Willcox Publisher Figure 6-4. As a reciprocating compressor moves back and forth, it draws in low-pressure vapor refrigerant and compresses it into high-pressure vapor refrigerant.