112 Video Game Design Foundations
appears smaller and darker? The 3D engine must make the object larger and
brighter as it gets closer to the viewer (the player).
To make an object larger as the player approaches it, the 3D engine
must scale the object. To scale an object, its dimensions are changed in a
way such that the object remains proportional. This is done by moving the
vertices of the object farther apart or closer together at the same rate.
In the example in Figure 4-24, the front (and back) face of each
original cube has been scaled to twice its original size (200%). The orange-
black cube is proportionally scaled. This means that all sides of the cube
also doubled in size. Notice how each side of the new cube has four check-
erboard squares on each edge. The original cube has two checkerboard
squares on each edge.
A B C
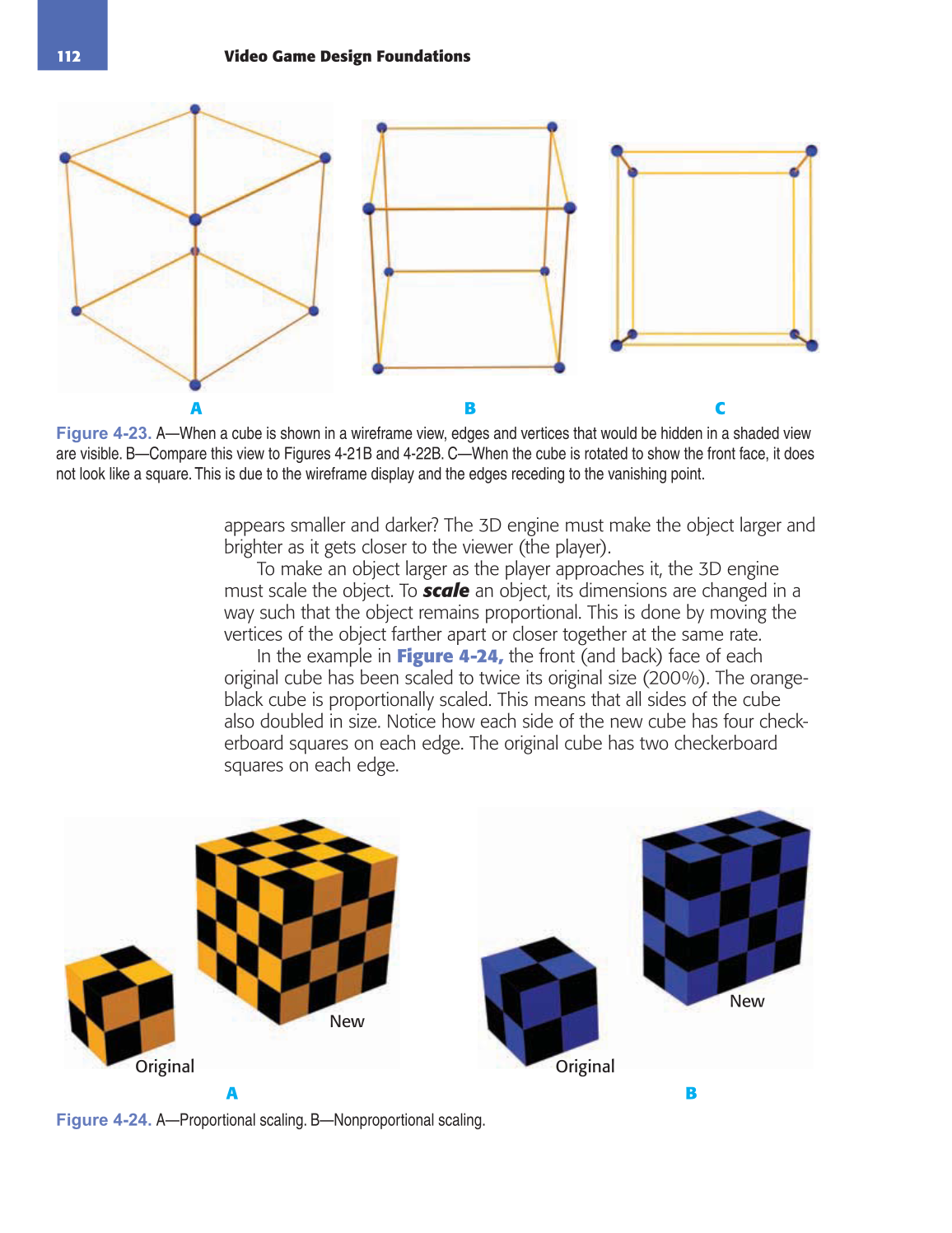
Figure 4-23. A—When a cube is shown in a wireframe view, edges and vertices that would be hidden in a shaded view
are visible. B—Compare this view to Figures 4-21B and 4-22B. C—When the cube is rotated to show the front face, it does
not look like a square. This is due to the wireframe display and the edges receding to the vanishing point.
Original
New
Original
New
A B
Figure 4-24. A—Proportional scaling. B—Nonproportional scaling.