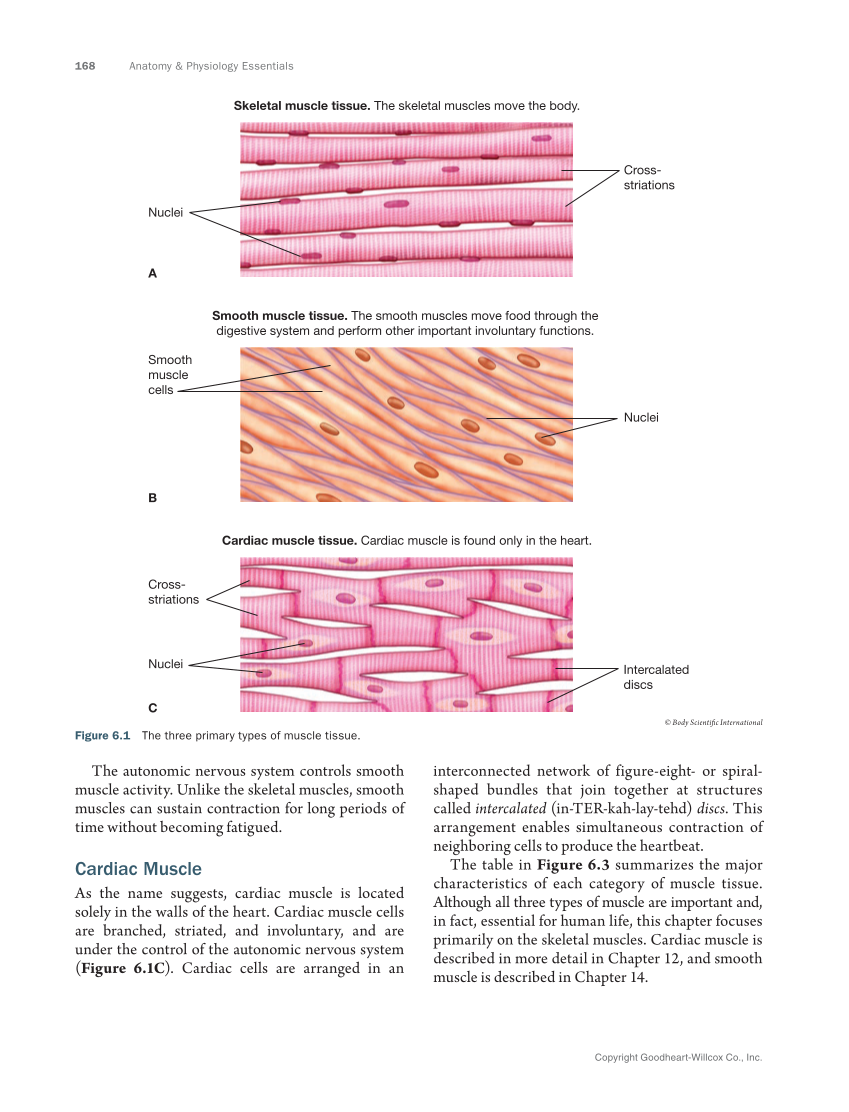
168 Anatomy & Physiology Essentials Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. The autonomic nervous system controls smooth muscle activity. Unlike the skeletal muscles, smooth muscles can sustain contraction for long periods of time without becoming fatigued. Cardiac Muscle As the name suggests, cardiac muscle is located solely in the walls of the heart. Cardiac muscle cells are branched, striated, and involuntary, and are under the control of the autonomic nervous system (Figure 6.1C). Cardiac cells are arranged in an interconnected network of figure-eight- or spiral- shaped bundles that join together at structures called intercalated (in-TER-kah-lay-tehd) discs. This arrangement enables simultaneous contraction of neighboring cells to produce the heartbeat. The table in Figure 6.3 summarizes the major characteristics of each category of muscle tissue. Although all three types of muscle are important and, in fact, essential for human life, this chapter focuses primarily on the skeletal muscles. Cardiac muscle is described in more detail in Chapter 12, and smooth muscle is described in Chapter 14. Nuclei Cross- striations Intercalated discs Cross- striations Nuclei Nuclei Smooth muscle cells Skeletal muscle tissue. The skeletal muscles move the body. Smooth muscle tissue. The smooth muscles move food through the digestive system and perform other important involuntary functions. Cardiac muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart. A B C © Body Scientific International Figure 6.1 The three primary types of muscle tissue.