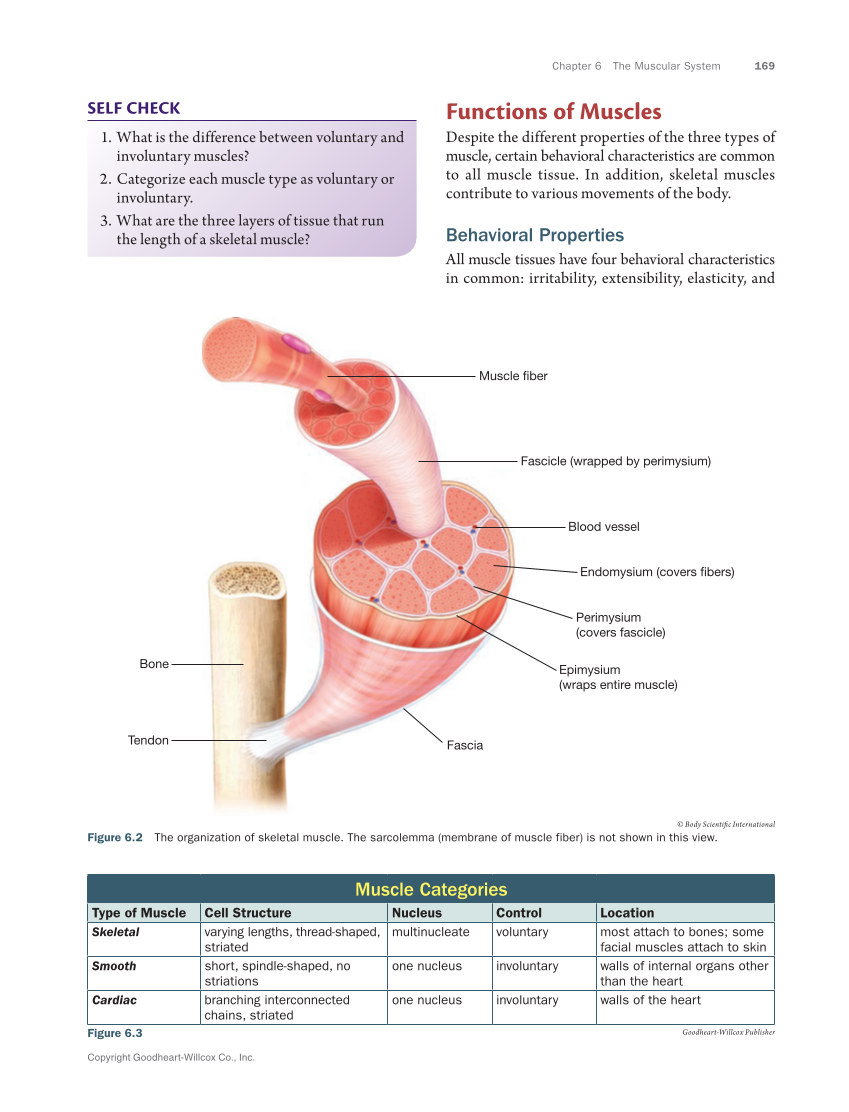
Chapter 6 The Muscular System 169 Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. SELF CHECK 1. What is the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles? 2. Categorize each muscle type as voluntary or involuntary. 3. What are the three layers of tissue that run the length of a skeletal muscle? Functions of Muscles Despite the different properties of the three types of muscle, certain behavioral characteristics are common to all muscle tissue. In addition, skeletal muscles contribute to various movements of the body. Behavioral Properties All muscle tissues have four behavioral characteristics in common: irritability, extensibility, elasticity, and Muscle fiber Blood vessel Fascia Perimysium (covers fascicle) Epimysium (wraps entire muscle) Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (covers fibers) Tendon Bone © Body Scientific International Figure 6.2 The organization of skeletal muscle. The sarcolemma (membrane of muscle fiber) is not shown in this view. Muscle Categories Type of Muscle Cell Structure Nucleus Control Location Skeletal varying lengths, thread-shaped, striated multinucleate voluntary most attach to bones some facial muscles attach to skin Smooth short, spindle-shaped, no striations one nucleus involuntary walls of internal organs other than the heart Cardiac branching interconnected chains, striated one nucleus involuntary walls of the heart Figure 6.3 Goodheart-Willcox Publisher