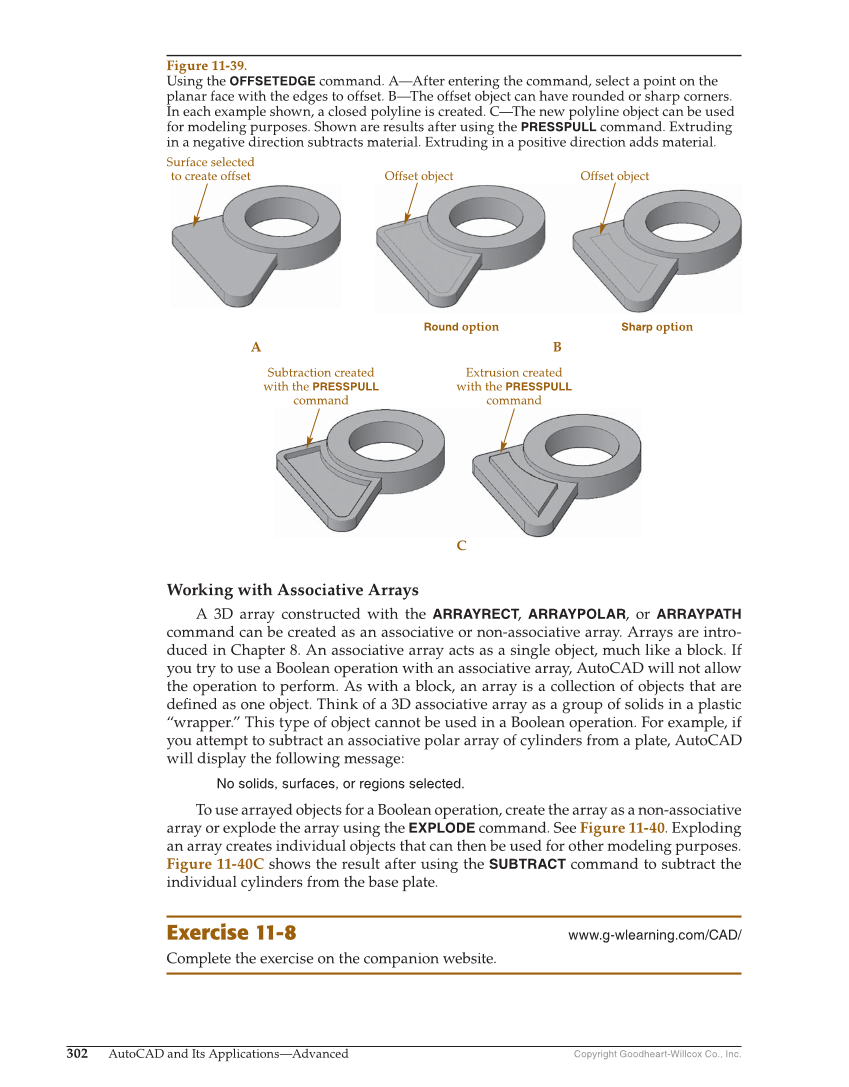
Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. 302 AutoCAD and Its Applications—Advanced Working with Associative Arrays A 3D array constructed with the ARRAYRECT, ARRAYPOLAR, or ARRAYPATH command can be created as an associative or non-associative array. Arrays are intro- duced in Chapter 8. An associative array acts as a single object, much like a block. If you try to use a Boolean operation with an associative array, AutoCAD will not allow the operation to perform. As with a block, an array is a collection of objects that are defi ned as one object. Think of a 3D associative array as a group of solids in a plastic “wrapper.” This type of object cannot be used in a Boolean operation. For example, if you attempt to subtract an associative polar array of cylinders from a plate, AutoCAD will display the following message: No solids, surfaces, or regions selected. To use arrayed objects for a Boolean operation, create the array as a non-associative array or explode the array using the EXPLODE command. See Figure 11-40. Exploding an array creates individual objects that can then be used for other modeling purposes. Figure 11-40C shows the result after using the SUBTRACT command to subtract the individual cylinders from the base plate. Exercise 11-8 www.g-wlearning.com/CAD/ Complete the exercise on the companion website. A B C Round option Sharp option Surface selected to create offset Offset object Offset object Subtraction created with the PRESSPULL command Extrusion created with the PRESSPULL command Figure 11-39. Using the OFFSETEDGE command. A—After entering the command, select a point on the planar face with the edges to offset. B—The offset object can have rounded or sharp corners. In each example shown, a closed polyline is created. C—The new polyline object can be used for modeling purposes. Shown are results after using the PRESSPULL command. Extruding in a negative direction subtracts material. Extruding in a positive direction adds material.