Chapter 6 The Nervous System 199
tiny sacs, or vesicles, that contain chemical
messengers called neurotransmitters (Figure 6.6).
Axon terminals do not actually touch the
other neuron or muscle, but are separated by
a microscopic gap called the synaptic cleft. This
intersection, including the synaptic cleft, is
known as the synapse (SIN-aps). A synapse
between an axon terminal and a muscle fi ber is
called the neuromuscular junction, as you learned
in chapter 5.
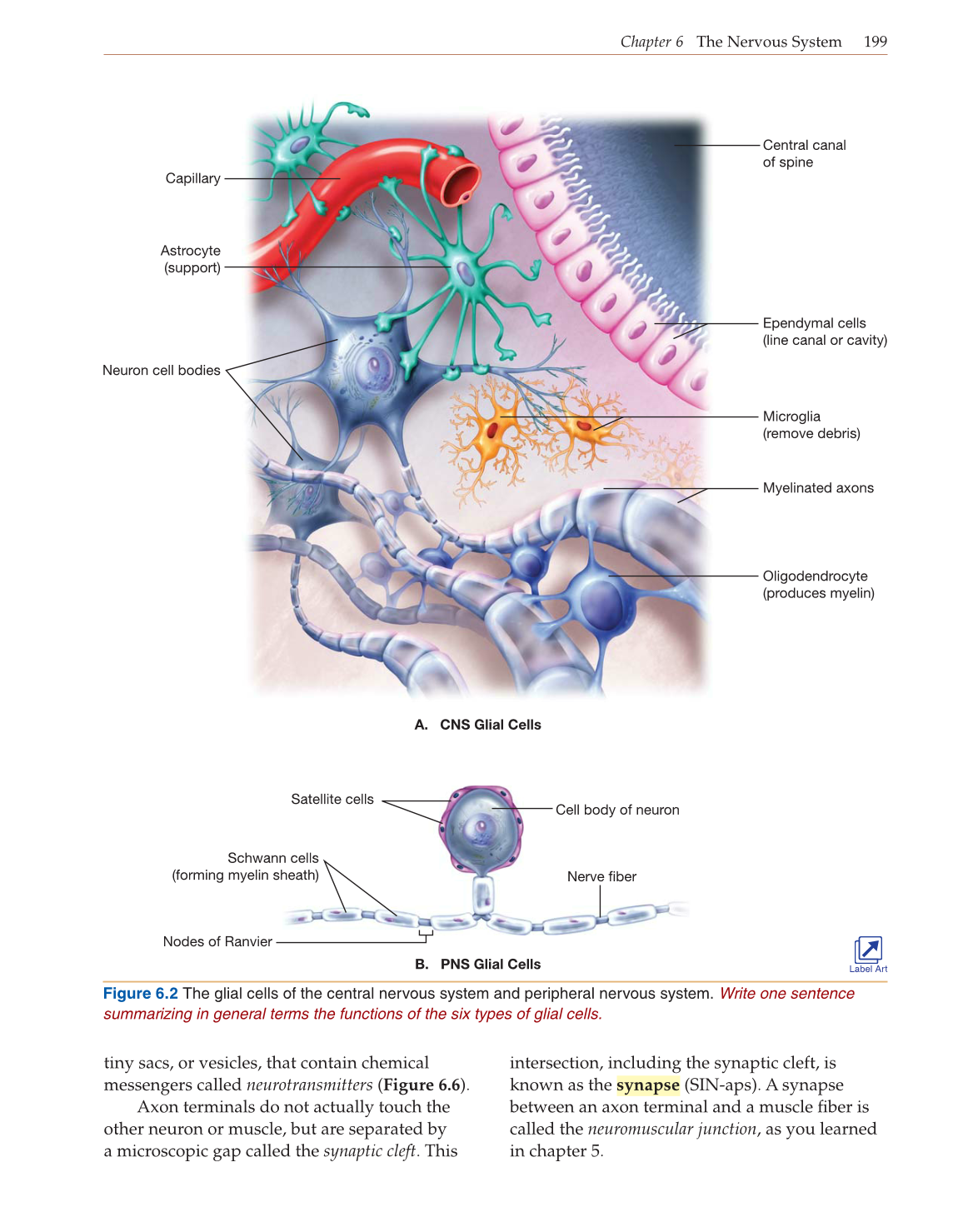
Figure 6.2 The glial cells of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Write one sentence
summarizing in general terms the functions of the six types of glial cells.
Microglia
(remove debris)
Myelinated axons
Satellite cells
Oligodendrocyte
(produces myelin)
Central canal
of spine
Ependymal cells
(line canal or cavity)
Nerve fiber
Schwann cells
(forming myelin sheath)
Cell body of neuron
A. CNS Glial Cells
B. PNS Glial Cells
Capillary
Astrocyte
(support)
Neuron cell bodies
Nodes of Ranvier
Label Art