200 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
When classifi ed by their function, there are
three types of neurons:
• Sensory (afferent) neurons carry impulses
from the skin and organs to the spinal cord
and brain, providing information about the
external and internal environments.
• Motor (efferent) neurons transmit impulses
from the brain and spinal cord to the
muscles and glands, directing body actions.
• Neurons that form bridges to transmit impulses
between other neurons are interneurons (inter-
NOO-rahnz), or association neurons.
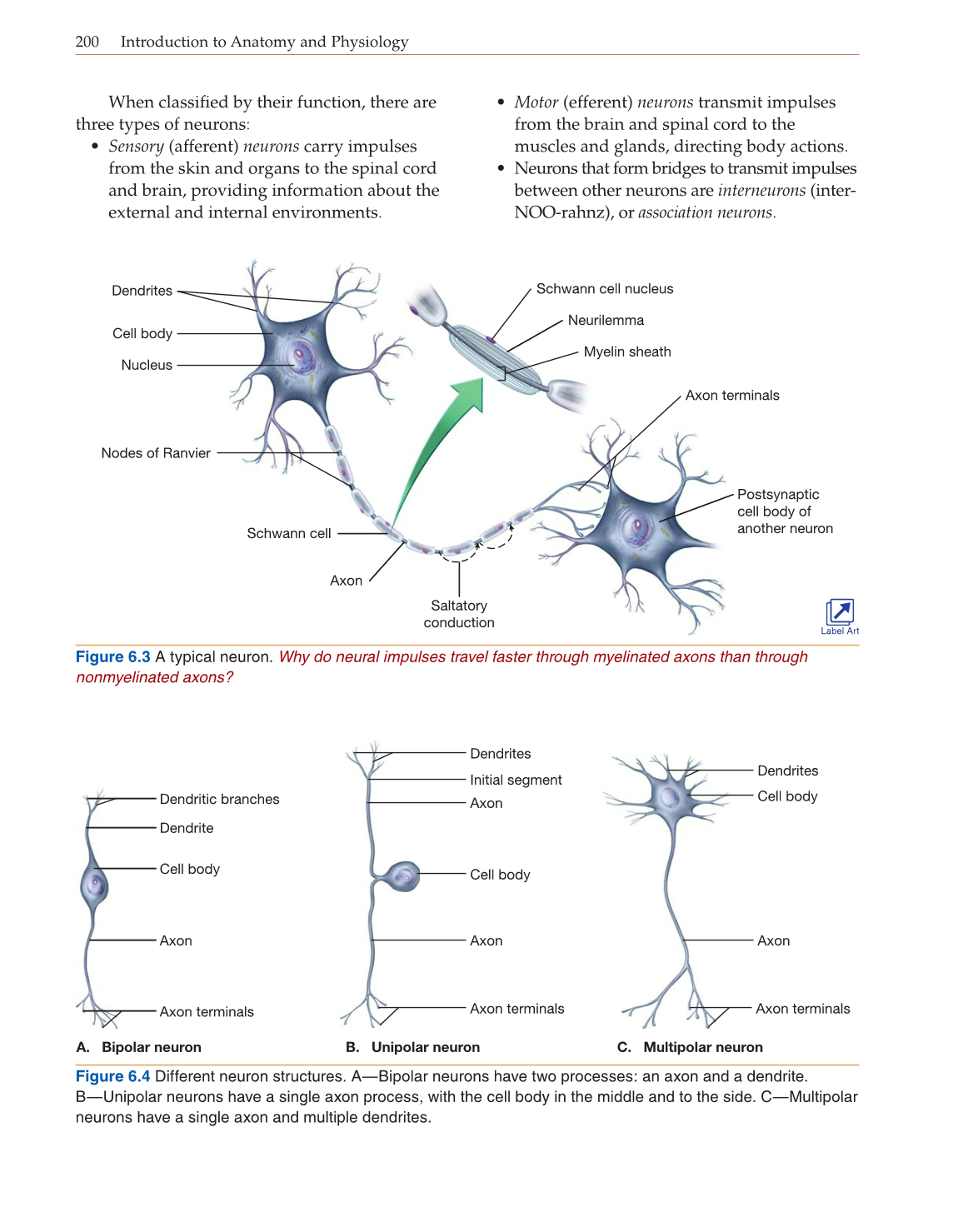
Figure 6.3 A typical neuron. Why do neural impulses travel faster through myelinated axons than through
nonmyelinated axons?
Dendritic branches
Dendrite
Cell body
Axon
Axon terminals
Dendrites
Initial segment
Cell body
Axon
Axon
Axon terminals
Dendrites
Cell body
Axon
Axon terminals
A. Bipolar neuron B. Unipolar neuron C. Multipolar neuron
Figure 6.4 Different neuron structures. A—Bipolar neurons have two processes: an axon and a dendrite.
B—Unipolar neurons have a single axon process, with the cell body in the middle and to the side. C—Multipolar
neurons have a single axon and multiple dendrites.
Schwann cell nucleus
Neurilemma
Myelin sheath
Schwann cell
Nodes of Ranvier
Saltatory
conduction
Axon
Axon terminals
Dendrites
Cell body
Nucleus
Postsynaptic
cell body of
another neuron
Label Art