56 Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics
• Will the insulation in a building affect the breath-
able air of its occupants?
Insulation codings
Insulations are marked with code letters indicating
their approved uses. Examples of these markings are HH
for high heat resistant, M for oil resistant, UF for
underground installation, etc. When selecting conductor
insulation, all conditions must be considered. A brief list
follows:
R Rubber
H Heat
HH High heat
A Asbestos
T Thermoplastic
M Oil resistant
UF Underground feeder
C Corrosion resistant
Conductor insulation may be color coded to assist
a technician in tracing it throughout a building or
throughout some other electrical application such as an
automobile. At times, the colors represent certain volt-
ages, polarities, or grounding conductors. The color used
is generally governed by building codes or manufacturing
associations. Uniform standards in the color coding of
insulators assist the technician in troubleshooting electri-
cal and electronic systems.
Types of Conductors
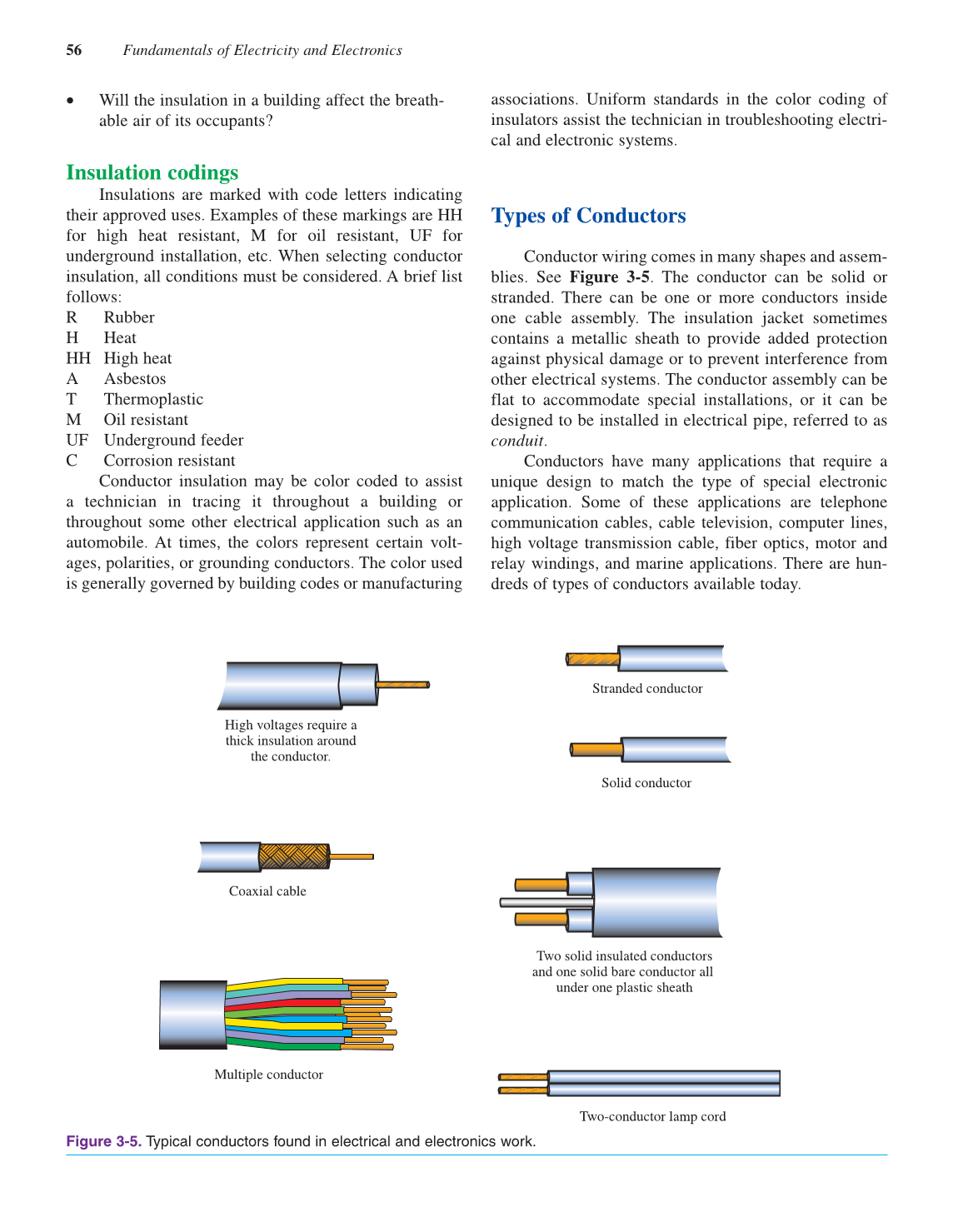
Conductor wiring comes in many shapes and assem-
blies. See Figure 3-5. The conductor can be solid or
stranded. There can be one or more conductors inside
one cable assembly. The insulation jacket sometimes
contains a metallic sheath to provide added protection
against physical damage or to prevent interference from
other electrical systems. The conductor assembly can be
flat to accommodate special installations, or it can be
designed to be installed in electrical pipe, referred to as
conduit.
Conductors have many applications that require a
unique design to match the type of special electronic
application. Some of these applications are telephone
communication cables, cable television, computer lines,
high voltage transmission cable, fiber optics, motor and
relay windings, and marine applications. There are hun-
dreds of types of conductors available today.
High voltages require a
thick insulation around
the conductor.
Coaxial cable
Multiple conductor
Two-conductor lamp cord
Two solid insulated conductors
and one solid bare conductor all
under one plastic sheath
Solid conductor
Stranded conductor
Figure 3-5. Typical conductors found in electrical and electronics work.